Introduction of multi story and high rise steel structure
- 23 Sep 2020
- steel structure

Types of steel structure of multi-story buildings
Features: Outstanding influence of lateral load effect: wind load, earthquake action
Classification: frame structure, frame-shear structure, tube structure
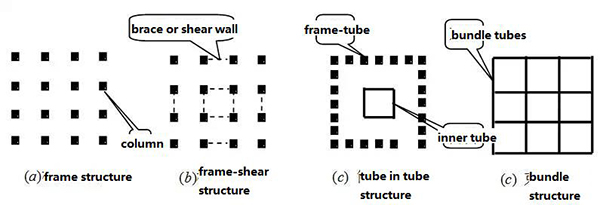
1. Frame structure features:
1.1 The plane layout is more flexible and the stiffness distribution is balance
1.2 The lateral stiffness is small, the ductility is large, the natural vibration period is long, and it is not sensitive to earthquake action, generally no more than 30 floors
2. Frame shear structure features:
2.1 Support or shear wall, dual fortification
2.2 No more than 40~60 layers
3. Features of cylinder structure:
3.1 The cylinder structure formed by the frame, the inner cylinder and other vertical members mainly bear vertical loads, and the outer frame mainly bears lateral loads
3.2 Rigid floor structure as the diaphragm of the frame tube
3.3 The shear lag causes the axial force of the corner column to be too large. Two measures: control the aspect ratio of the frame tube plane; increase the ratio of the linear stiffness of the frame tube beam to the column
3.4 The applicable building height can exceed 90 floors
4. Tube-in-tube structure
4.1 Mitigating the shear lag effect of the frame-tube structure
4.2 Dense column deep beam or reinforced concrete inner tube
5. Applicable height
According to the seismic fortification intensity:
Applicable height of steel structure and steel structure high-rise building with concrete shear wall (m)
| Structure type | Structure system | Non-seismic fortification | Seismic fortification intensity | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 6, 7 | 8 | 9 | |||
| Steel structure | Frame Frame-support (shear wall panel) Various barrels |
110 260 360 |
110 220 300 |
90 200 260 |
50 140 180 |
| Steel structure with concrete shear wall | Steel frame-concrete shear wall Steel frame-concrete core tube |
220 | 180 | 100 | 70 |
| Steel frame tube-concrete core tube | 220 | 180 | 150 | 70 | |
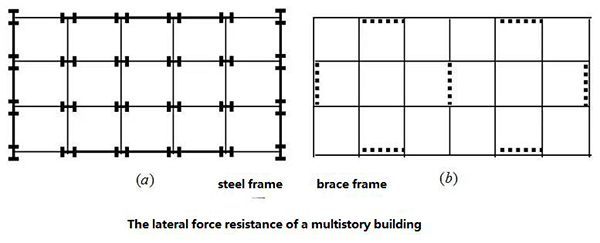
5. Non-seismic fortified multi-storey (£12 storey) steel structure house form:
5.1 Pure use of frame structure or diagonal bracing (or shear wall) system
5.2 The connection of the beam and column of the diagonal bracing system can be made into hinged support, that is, flexible connection
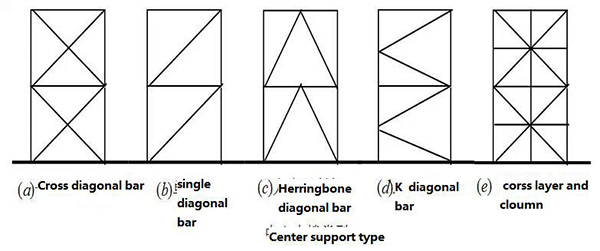
6. Forms of multi-story and high-rise steel structure buildings for seismic fortification:
6.1 Central support system, no more than 12 floors
6.2 Eccentric support system, more than 12 layers
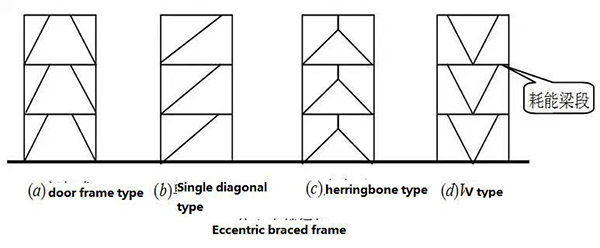
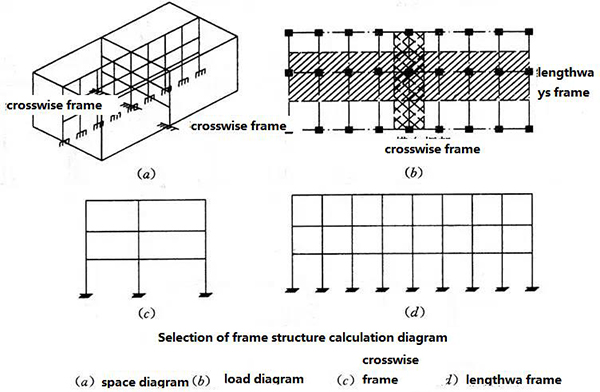
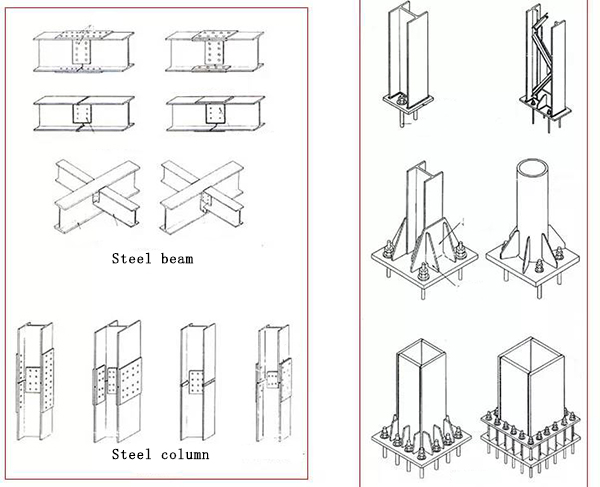
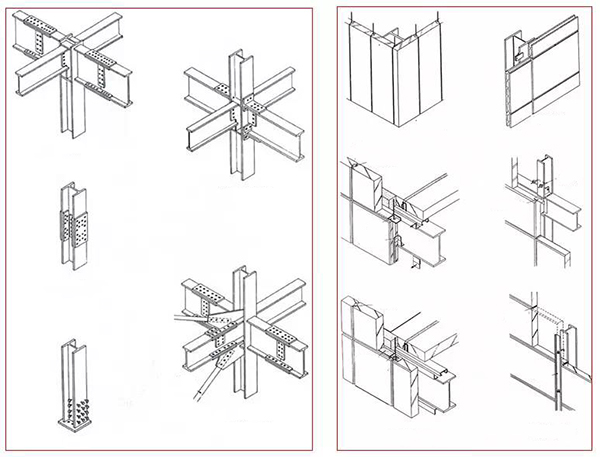
7. Summary of structural layout
7.1 Convex plane form of smooth curve: small wind carrier type coefficient
7.2 Adopt a centrally symmetrical or biaxially symmetrical plane form: reduce or avoid torsional vibration under wind load
7.3 Plane size relationship
L, l, l’, B’ limiting value
| The aspect ratio of the plane | Aspect ratio of uneven part | Large opening width ratio | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| L/B | L/Bmax | L/b | L’/Bmax | B’/Bmax |
| ≦5 | ≦4 | ≦1.5 | ≧1 | ≦0.5 |
8. Irregular plane structure
Structure vertical layout
9. foundation
9.1 Basement should be installed
9.2 The buried depth of the seismic fortification foundation should be consistent, and local basements should not be used
9.3 The buried depth of the foundation, the natural foundation should not be less than H/15, and the pile foundation should not be less than H/20
9.4 Use reinforced concrete shear wall or frame shear structure type
9.5 Set the transition layer of steel frame (steel) concrete, generally 2~3 layers