Large-span space steel structure
- 01 Jun 2020
- steel structure
1. Description
Large-span space steel structure are mainly used in public buildings, such as city halls, theaters, exhibition halls, concert halls, gymnasiums, stadiums and airports.
Large-span structures are also used in industrial buildings, such as general assembly workshops of aircraft manufacturing plants, hangars, hull structure workshops of shipyards, etc. The use of large-span structures in these buildings is determined by the large size or process requirements of the assembled machines (such as ships and aircraft)

There is no unified measurement standard for the span of large-span structures. The Chinese standards "Code for Design of Steel Structures" and "Specifications for Design and Construction of Grid Structures" define a large-span structure above 60m, with special provisions for calculation and construction. In China, the maximum span is 153m currently, and the cable-membrane structure made of steel cables and membranes has a maximum of 320m.
The long-span structure mainly works under dead weight load, the main contradiction is to reduce the dead weight of the structure, so the steel structure is the most suitable choice. Light roof structures and light roof materials should be used in large-span roofs as much as possible, such as color-coated profiled steel plates and profiled aluminum alloy plates.
2. Mainly divided into two categories:
Plane structure system: beam system, frame system, arch system
Space structure system: grid and net shell structure, suspension cable structure, membrane structure
Firstly introduce several types of plane structure systems in the below.
3. Plane load-bearing large-span steel structure
3.1 Beam structural system
The beam structural system generally adopts the form of a simple-supported truss. The advantage of the truss is that it is relatively simple to manufacture and install. The upper and lower chords and the web only bear tensile or compressive forces, and there is no lateral thrust on the support.
Applicable span: 40-60m, larger span is not economical due to excessive steel consumption.
The focus is on the layout of the support system, which is very important to ensure the overall rigidity of the whole structural system.
The shape and web system of the large-span beam structure are determined by the span, roof type and suspended ceiling structure. Trapezoid and arch truss are commonly used. The height-span ratio of the truss determined by optimal weight is generally 1/6 to 1/8.
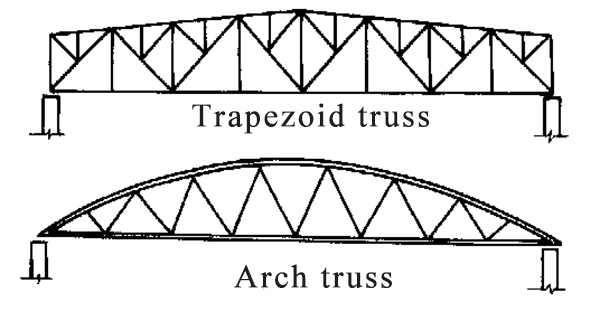
Commonly used type:
(1) Angle steel (or T-shaped steel) truss
(2) H-shaped steel heavy truss
(3) Steel tube truss (round steel tube or rectangular tube)
The difficulty of truss design is in the nodes and supports. When the span is greater than 35-40m, one of the supports of the beam structure must be made movable to reduce the lateral reaction force transmitted to the supporting wall or column. The lateral reaction force is generally produced by the elastic deformation of the lower chord of the roof truss.
3.2 Frame structural system
Compared with the beam structural system, the frame system is more economical, and the height of the beam can be smaller than that of the beam structure, and the rigidity is also larger, which is often used in industrial buildings.
The frame column footings can be made into hinged or rigid. The hingeless frame has better rigidity, saves steel and is easy to install, but this frame is more sensitive to temperature and has higher requirements for foundation.
There are two main types of solid-web and lattice.
(1)Solid-web type frame structural system
The solid-web frame is suitable for the frame structure with a smaller span (L = 18 ~ 60m). It has the advantages of simple production, easy transportation, which can also lower the house height. Solid-web frames are often designed as hinged column footing.
Due to the unloading effect of the bending moment of the frame support, the height of the beam of the solid-web frame is not large, and the span can be taken from 1/30 to 1/40.
The lightweight portal rigid frame structure, which has been vigorously developed, is a kind of solid-web frame structure system. It is characterized by the use of profiled steel plates for the both roof and walls, and the structure mainly bears its own weight.
(2) Lattice type frame structural system
When the span is greater than 60m, the solid-web frame is not economical. In this case, the lattice structure will be used, and the maximum span can be 150m.
Usually designed as a variable cross-section, the high-span ratio of the frame beam is selected in the range of 1/12 to 1/20.
Calculation of internal force and deformation
When the span is not large, the lattice general frame can take the converted stiffness and convert it to its equivalent solid- web frame to calculate the internal force. When the span is large, the deformation of all webs must be considered for calculation.
3.3 Arch structural system
The arch structure is beautiful in appearance, reflecting the perfect combination of structural stress and architectural styling, which is an important type of large-span steel structure.

Features of the arc
(1)The arch body mainly bears the axial force. When the span is large (such as more than 80 ~ 100m), it is more economical than the beam structure and frame structure.
(2)There are two hinged arches, three hinged arches and no hinged arches. The most used is the two hinged arch, which has the advantages of simple installation and manufacturing, free rotation of the hinge, and lower temperature stress. The distribution of bending moments in a span for no hinged arch is the most favorable, but it requires a strong foundation and the temperature stress is also larger.
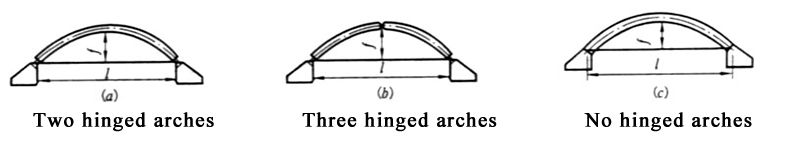
(3)The horizontal thrust of the arch is greater, which has a higher requirements for the support. In order to reduce the horizontal thrust, horizontal rods or rubber bearings can be set.
In the stamped stadiums, exhibition halls and hangars, the support of the arch are often the walls or stands, etc of the house. If there is no horizontal wall or grandstand, it is required to set the buttresses to withstand the horizontal thrust of the arch.
(4)The arch section is divided into two types: solid-web type and truss type, which are generally of equal section. The bending moment of the arch body is small, so the height of the section is not large. The solid-web type can take l / 50 ~ l / 80, and the truss type can take l / 30 ~ l / 60.
The arch section can be H-shaped steel, double angle steel, T-shaped steel, channel steel, round steel tube and square steel tube.
Arch design
(1)The shape of the arch axis should be as close as possible to the pressure curve. When the symmetrical and evenly distributed loads along the arch chord play a major role, a quadratic parabola (close to the bending moment diagram) should be used. In order to simplify the design and manufacture of the arch, it can also be replaced by a circular arc, which will not cause substantial changes in the internal force of the flat arch. For high arches with large dead weight, catenary profile should be adopted. Under the effect of wind load, due to the large change of the pressure line, the shape of the arch should take the middle of the two extreme pressure lines.
(2)Wind load is a very important load in the calculation of arch structures. In particular, attention should be paid to the influence of wind suction on the arch structure, and consideration should also be given to the situation of side wind pressure or end wind pressure on buildings.
(3)The plane arch structure is a compression curved rod, which should be designed by bending rod. The arch needs to be checked with the strength and stability in the bending moment action plane. Because it is difficult to calculate the differential equation of the curved rod balance, at present, the critical force of the rod can only be approximated calculated according to the elastic method. Currently, there is no provision for the calculated length of the curved rod. The calculated length coefficient of the arch is related to the shape of the arch, the ratio of the vector height f of the arch to the ratio of the arch span l
(4)If the stiffness of the arch outside the plane of the bending moment is very different from that in the plane, it will easily cause out-of-plane instability when compressed. The lateral support system and purlin system along the length of the house should be used as the out-of-plane support point. At the same time, the stability of the out-of-plane plane should also be checked according to bending rod.
(5)The support hinge of the arch can have different types.
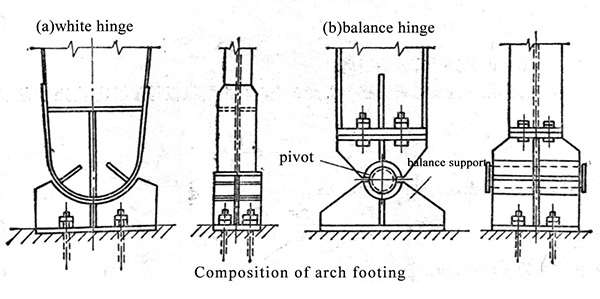
(6)The dome hinge in the three-hingeed arch is a difficult in structural design. The latticed arch needs to be changed to a solid-web section at the location of the bearing hinge and the dome hinge. At the same time, appropriate stiffeners must be set to transfer bigger concentrated reaction.
